GIACIS
Geodata for Innovative Agricultural Credit Insurance Schemes in Ethiopia
> Download the GIACIS project closure flyer
The objective of the GIACIS (Geodata for Innovative Agricultural Credit Insurance Schemes) was to enable smallholder farmers to cope with and manage weather-related risks. GIACIS targeted Ethiopian smallholder farmers in four key-regions of Ethiopia: Oromia, the Southern Nations, Nationalities, and Peoples’ Region (SNNPR), Amhara and Tigray, cultivating teff, wheat, barley, maize and sorghum.
In the Ethiopian highlands the poorest farmers are in need of microcredit to buy seeds and fertiliser. In the case of crop failure, which happens often, farmers have no income and still have to pay back the loan. To help tackle this problem, GIACIS offers farmers affordable insurance based on satellite data.
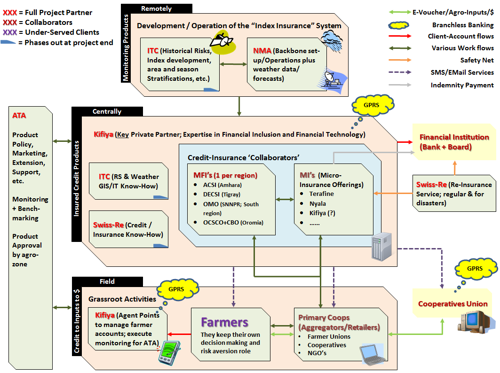
The GIACIS partnership consisted of Faculty for Geo-Information Science and Earth Observation (ITC) at the University of Twente in the Netherlands as lead partner and the Ethiopian organisations Agricultural Transformation Agency ATA (as technology partner), Kifiya Financial Technology (as credit and insurance provider) and the National Meteorological Agency NMA (as information provider).
Provided services
GIACIS has developed and implemented a single-peril drought insurance product named “VICI” that is based on vegetation indexes. The VICI toolbox is used to derive a greenness indicator, called the Normalised Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) from the Copernicus NDVI-product disseminated through the EUMETCAST system, currently using the Sentinel-3 Ocean and Land Colour Instrument (OLCI) on a 10-day basis. The toolbox facilitates import, aggregation, pre-processing and temporal filtering routines (incorporating future NDVI 10-day climatology time steps). The results are transformed to a table to be ingested in the insurance scheme by the Ethiopian partners. A time series of satellite datasets that goes back more than 20 years is used to for historical analysis and simulation.
Farmers can purchase this insurance product to insure their agricultural inputs against crop loss caused by drought events. Drought maps of each season are made and translated into pay-out maps to determine pay-out per insured farmer according to their geolocation on the map. In principle this product is applicable to any arable crop.
Business model
The product is sold through direct sales of insurance policies via brokers. In 2016 the product became the first official insurance product approved by the National Bank of Ethiopia, and put under management of a national public-private partnership (PPP) consisting of the Ethiopian partners mentioned above. This coupling of the insurance service with microcredits provided by the Ethiopian government was done to increase the uptake of the insurance service, to reach scale of economies and reduce insurance charges for farmers. However, the introduction and scale up got delayed several times due to the unstable political situation in the country.
The roles for the ownership and continuation of the services have been decided on and approved by the partners: ATA is the product owner and Kifiya has an executive role and implements and maintains the service. Both organisations attracted a new partner called Global Green Growth Institute (GGGI) to establish an agricultural facility fund that will contribute to scaling up of the product by providing a premium subsidy to farmers and financial support to insurance companies in the case of losses beyond their capacity. Satellite processing activities are at present fully embedded into the NMA daily operations as information provider to Kifiya. NMA is assisted by Mekelle University for validation and maintenance of VICI drought insurance product (and by VITO, the Flemish technology research institute, during the conflict period). Kifiya reported that face-to-face interaction is the best method to reach non-literate communities. The objective of the insurance companies in the project is not to generate profit, but to test whether the product and the ecosystem in general are working.
Impact
GIACIS made an important step towards scaling up of crop insurance in Ethiopia by getting the national government on board to adopt the product as their national crop insurance programme, which provided a licence-to-operate and opportunities for growth.
Scaling up of the service was substantially hampered due to local unrest (the state of emergency was proclaimed twice during the project) and changing political priorities. In addition, the operation of the agent network proved to be not optimal, the premium to be paid was considered unaffordable and reinsurance was difficult. All these problems were tackled during and after the end of the project.
Although there were some good growing seasons, during the 2015/16 and the 2016/17 seasons, different regions of Ethiopia experienced severe droughts.
When the project closed in 2018 a total of 7,735 farmers had bought a drought insurance policy. An estimated 2 million farmers in 40 districts of Ethiopia have been reached and informed. Activities continued with support of the European Commission and the Japanese development agency JICA. This resulted in a continuing expansion of operations. In 2020 a partnership was established with Wasasa, a large microfinance institution, and in 2022 with the Oromia Insurance Company.
Partnership
Partners are mutually very complementary and as group all-inclusive:
Lead Partner:
- ITC University of Twente, The Netherlands
Partners:
- Business partner: Kifiya Financial Technology PLC, Ethiopia.
- Corporate partners: Agricultural Transformation Agency – ATA, Ethiopia.
- National Meteorology Agency of Ethiopia – NMA
- Support partner: Swiss Re corporate solutions –Switzerland
Aligning micro-insurance to the logic of the Rural Finance Strategy (RFS) program of ATA has the advantage that roles and responsibilities of all partners can be optimally defined and effectuated.
The GIACIS partnership:
> Visit the reporting tool for project results and updates

Kifiya’s branchless banking technology: twice weekly, an agent will be available at the market place of a village for farmers to make transactions through GPRS.
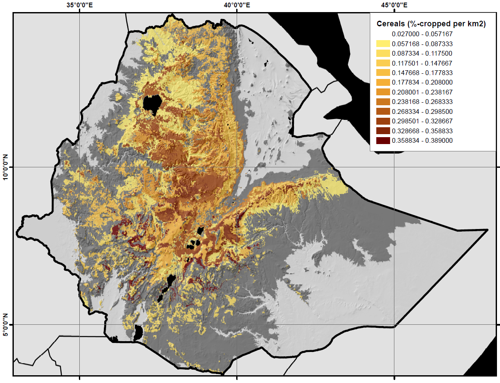
The GIACIS project area: all highland areas where the 5 key cereals are cultivated (Tef, Wheat, Barley, Maize, Sorghum).
| Country | Ethiopia |
| Services | Crop index insurance |
| Crops | Various |
| Target groups | Farmer (smallholders)Insurance company |
| Project period | 2014-2018 |